REGARDS Microservices architecture
Microservice architecture
To meet CNES requirements, REGARDS deploys a set of business services within a distributed and modular microservices architecture.
These microservices are highly cohesive and loosely coupled Restful web services, interacting inside the cluster using synchronous (REST through HTTP protocol) and asynchronous (event bus through AMQP protocol) communications.
Each microservice is structured in modules, being themselves structured in layer architecture. Each service matches an elementary REGARDS function (single accountability), and has its own execution context and its own configuration ( modularity). It is built, tested and deployed separately from other services (modularity, maintainability, scalability) and exposes a REST API (HATEOAS) which relies on a service contract.
Such granular architecture ensures we can provide a strong horizontal scalability. Several instances of the same service can be simultaneously deployed on the system, allowing it to bear load spin-up thanks to the “load balancing” mechanism. Such functionality allows the system to be highly fault-tolerant and resiliant to load fluctuation. On top of that, GUIs are built using responsive web architecture.
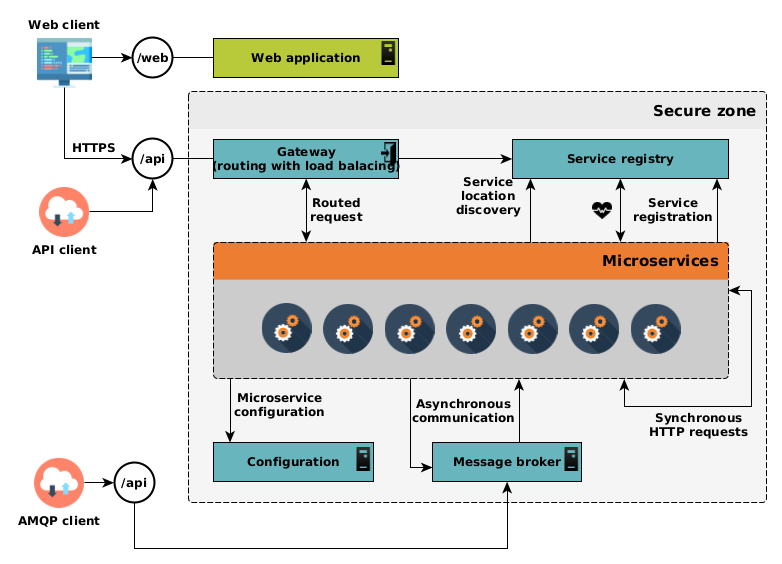
The here-above diagram describes principles of such architecture.
REGARDS microservices are surrounded by several components : a gateway providing a single point to allow external world
to interact with our system, a discovery and registration service to let service know each other and load balancing; and
finally a centralized configuration holding each kind of microservice configuration.
The key points are that all microservices are stateless and expose a REST API over HTTP and an AMP API. See REST API Concept and AMQP API Concept to learn more about the way Regards manage both API.
Non fonctionnal microservices architecture
Non fonctionnal microservices are listed here under. Those mandatory microservices are deployed to manage microservices stack architecture.
- rs-registry : Microservices registry.
- rs-config : Microservices centralized configuration provider.
- rs-gateway : Microservices main access point
- At startup each REGARDS microservices retrieve their configuration from rs-config microservice.
- Once they have successfully booted, REGARDS microservices register to rs-registry microservice.
- Client access REGARDS microservice through rs-gateway microservice. rs-gateway microservice, ask for target microservice address to rs-registry and redirect request to it.
Regards Microservice core architecture provides two types of API :
REST API: You can submit REST HTTP Requests to Regards microservices through rs-gateway microservice.AMQP API: You can submit and subscribe to the Regards Message Broker : RabbitMQ.
Both API types will be described for each microservice with API Guides under Services section of this documentation.