How it works
The config microservice is based on Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka.
Spring Cloud Eureka is used for two purposes:
Microservice registry
In a microservice architecture, it's crucial for each service to discover and
communicate with others without needing to know their exact network locations or addresses.
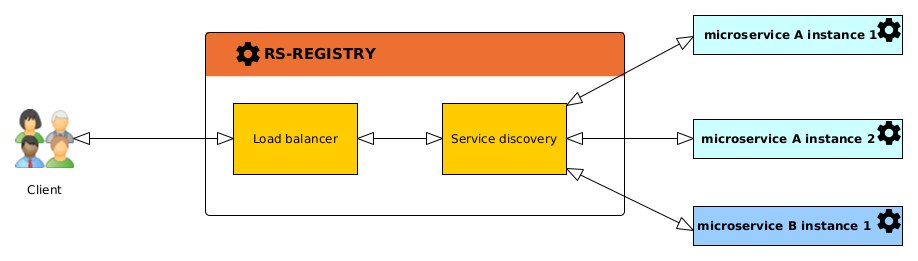
A microservice registry enables microservices to dynamically discover and communicate with each other
without needing to know the addresses of other services in advance. This simplifies scalability, deployment
management, and system resilience by allowing reliable and flexible communication between microservices.
the Eureka server (the rs-registry microservice) fulfills this role by centralizing information about available
services.
The main concepts used are:
-
Service Registration: Each microservice, when it starts up, registers itself with the Eureka server by sending its IP address, port, and other necessary metadata. This allows the Eureka server to maintain an up-to-date list of all available services.
-
Service Discovery: When one microservice needs to communicate with another, it queries the Eureka server to obtain the location (URL) of the target service. This allows dynamic resolution of the service address, which is particularly useful when service instances can scale up or down or move within the network.
Load balancing
Spring Cloud Eureka also plays a key role in load balancing within a microservice architecture. When a service is deployed with multiple instances (for scalability or redundancy), it's important to distribute incoming requests evenly across these instances to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization.
When a client service queries the rs-registry microservice to find a target service, the Eureka server provides a
list of all active instances, then uses this information to distribute requests across the available
instances. This ensures that no single instance is overwhelmed with too many requests, improving overall system
reliability and responsiveness.