How it Works
Introduction
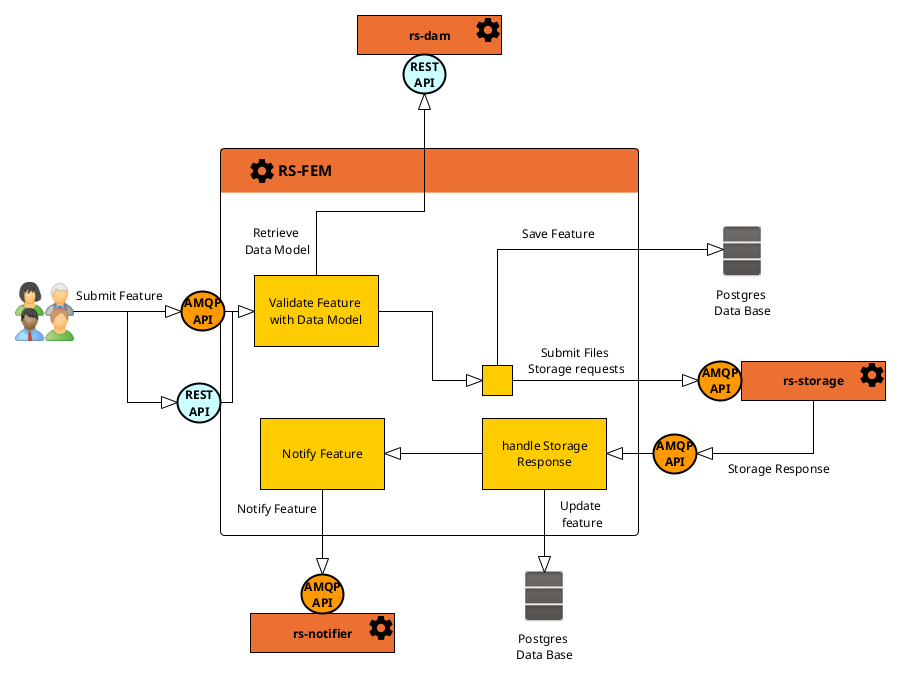
Products creation requests can be submitted as Features with GeoJSON formatted requests
through AMQP API or
REST API to rs-fem microservice.
AMQP API is strongly recommended to increase service performances when a big amount of requests is sent.
When a Feature request is received (AMQP or REST API), the request is saved in the microservice database and will be processed by schedulers and Jobs as described in the global architecture overview.
The diagram below explains how a product creation request is processed.
Throughout the processing of a request in the service, the status of the request changes. The diagram below shows the possible states and the transitions between them.
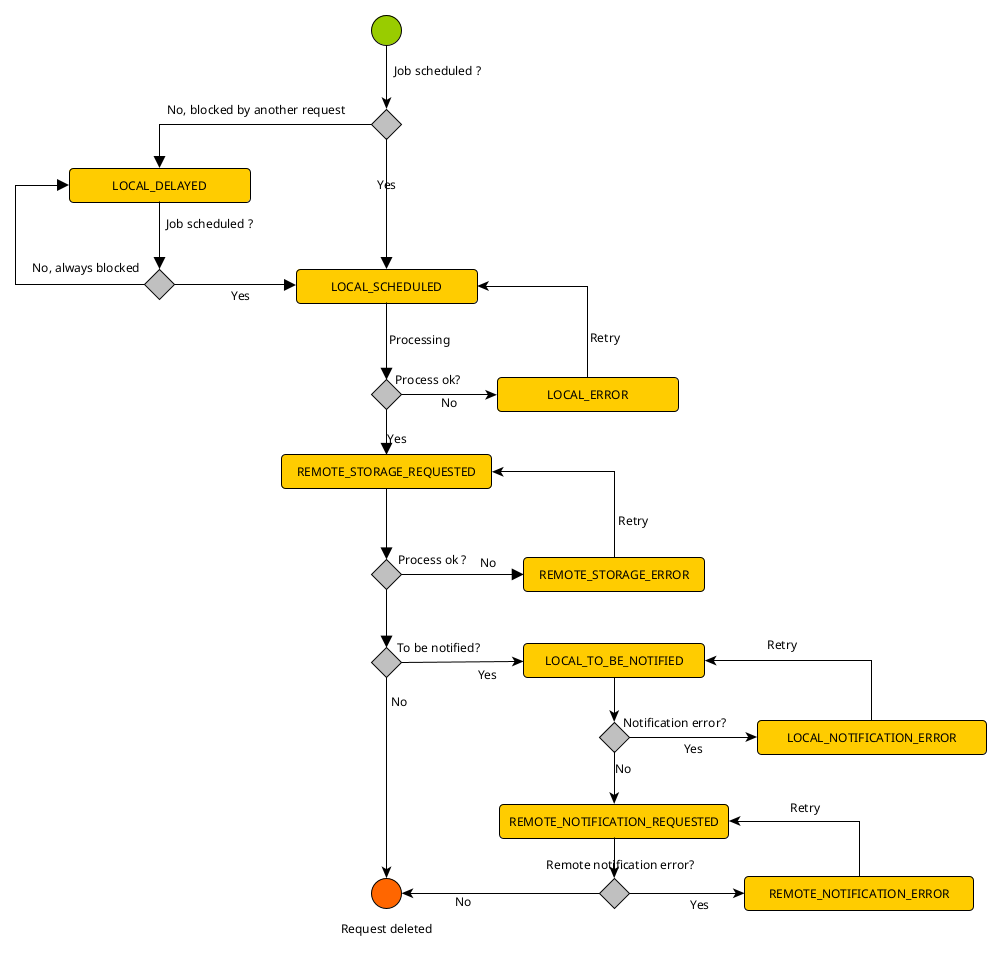
Request priority
When submitting a request to create, modify, delete or notify products, you can specify the priority of your request. There are three priorities: HIGH, NORMAL and LOW.
Giving your request a high priority ensures that it will be processed by the service before requests with lower priorities.
Products metadata validation
Submitted Feature requests must provide an associated Data Model in their metadata section.
To validate this model, rs-fem microservice keeps a cache of Data Models retrieved from the rs-dam
microservice.
Model validation checks for attributes in properties.descriptiveInformation section of the SIP. They have to be compliant with attributes defined in the given Data Model. Validation checks for:
- Mandatory attributes,
- Attributes values types
- Attributes values restrictions
Attributes of the data model are validated with case sensitive on attributes labels.
Products versioning
To understand versioning, you must be familiar with the two different identifiers of a feature in the rs-fem service.
- Provider identifier (or
providerId) : Is an arbitrary identifier provided by the feature creator owner. It is not a unique identifier for the service, but is used to handle product versioning. - Uniform Resource Name (or
urn) : Is the unique identifier of a feature.
The rs-fem representation of URN is
URN:FEATURE:<type\>:<tenant\>:<uuid\>:V<version\> with :
- type :
DATA,DATASETorCOLLECTION - tenant: tenant or project in which the product is created.
- uid: Universally unique identifier. Generated from the feature given providerId
- version : entity version
"urn":"URN:FEATURE:DATA:project1:c6487db8-9955-3917-a7e2-0374ccde903c:V1"
When updating a Feature with a request, the rs-fem microservice may deal with Feature versioning.
There are several possibilities to update a request, leading to different versioning policies:
- If a Patch request is used with an existing feature urn, the product is simply updated, its version is not incremented. To learn more on how to patch a product see AMQP Guide or REST Guide.
- If a Creation request is used with the same providerId as an existing one, then a new feature is created with
an incremented version number. If the override parameter in the request metadata is set to
true, then the old versioned feature is deleted after the new one creation success. To learn more on how to create a product see AMQP Guide or REST Guide. - If a Creation request is used with the same providerId and urn as an existing one , it means that a
feature with the same version already exists. Then, we need to check the updateIfExists parameter in the request
metadata :
- If it is set to
true, then the feature is updated, like a patch request. - Otherwise, an error is raised.
- If it is set to
Mainly, there is two ways to handle versioning in rs-fem service :
- Let the service manage the versioning and only provide the provider identifier (providerId)
- Manually handle product versioning by providing unique urn in the request metadata.
Product Associated files
Creation
When you ask the rs-fem microservice to create a new product,
you can choose between two methods to handle associated files:
- Storage : You want Regards system to move associated files to one or many configured storage locations.
- Reference : You want Regards system to reference associated files with there current location and without moving them.
In both case, the product associated files wil be added in the rs-storage microservice file referential.
If your product contains associated files, it will not be fully created until the storage service has correctly
processed the files and added them to its repository.
To know how to select file management in a creation request see AMQP Guide or REST Guide.
Like product metadata, the files associated with a product can be modified. To know how to modify product files see AMQP Guide or REST Guide.
Update
When you request a product update and specify associated files, by default the service will add these files to the existing ones. However, if you use the AMQP API, you can specify the file update mode. The available modes are :
- REPLACE: Deletes existing files and adds new ones.
- APPEND: Adds the supplied files to the existing files.
Products dissemination
How to ?
If the rs-fem microservice is configured to notify external components, each created/modified/deleted
feature is sent to the rs-notifier microservice for notification to external components.
To notify external systems you need to:
- Activate automatic notifications of products in the Feature manager configuration
- Configure the wanted recipient(s) of the notifications in the Notification service configuration
Nevertheless, if automatic notifications is not activated, you can manually notify selected features through admin UI.
When a notification is sent to a recipient by the rs-notifier service, the dissemination information of the feature is
updated by the rs-fem microservice with the following parameters:
- recipient label: Name of the notification's recipient (as configured in
rs-notifierservice) - dissemination date: Date of the notification
- acknowledge date: Date of received acknowledgement. If the recipient is not configured to send acknowledgements,
this date is the same as the dissemination date. If the recipient is configured to send acknowledgements, this
date is the date on which the acknowledgement is received. This acknowledgement parameter is configured in the
rs-notifierservice for each recipient.
With this information, Regards administrators can see through administrator UI all recipients of features notifications.
Products notification format
To understand how rs-notifier can handle product notifications received from the rs-fem microservice, here is the
format of each product notification between rs-fem and rs-notifier :
{
"metadata": {
"action": "UPDATED",
"sessionOwner": "",
"session": "",
"changedAttributes": [
"properties.system.archive_url",
"files"
]
},
"payload": {
"type": "Feature",
"urn": "",
"entityType": "",
"model": "",
"last": false,
"history": {
"createdBy": "",
"updatedBy": "",
"deletedBy": ""
},
"geometry": {},
"bbox": [],
"crs": "",
"files": [
{
"locations": [
{
"storage": "",
"url": ""
}
],
"attributes": {
"dataType": "RAWDATA",
"mimeType": "text/plain",
"filesize": 97
}
}
],
"properties": {
"system": {
"archive_url": "s3:/storage5566/82653"
}
}
}
}
The payload section contains the product that has been notified and the metadata section contains the following information:
| Parameter | Type | description |
|---|---|---|
| action | String | Indicates the action on the product that triggered the notification. Possible values are CREATED, UPDATED, DELETED, ALREADY_DELETED, NOTIFIED. |
| sessionOwner | String | Session Owner that created the product |
| session | String | Session in which the product was created |
| changedAttributes | String[] | List of payload attributes that are updated (set, modified or unset). Only defined when action is UPDATED. The list of attributes is limited to files and any sub-fields of properties. See the example above. |
You can then use this information (metadata and payload sections) to configure the rs-notifier service to send the feature to the required recipients.
Products dissemination acknowledgement
External systems who subscribe to Feature notifications from the rs-fem service can send back an acknowledgement to
inform that the notification has been successfully handled. To do so, refer
to Feature notification acknowledgement guide.
With this system, Regards administrators can validate through administrator UI that notifications has been successfully handled by recipients.
Delaying the processing of requests
When you submit a product request to the rs-fem microservice, you can ask for them to be processed at
a later date. To do this, you need to specify the date on which you want the treatment to be carried out.
Please refer to the various API guides to find out how to specify this date in your requests.